2024智慧树网课答案 Math model of metal heating under action by laser beam 最新完整智慧树知到满分章节测试答案
第一章 单元测试
1、 问题:Steps at the math modeling are( )。
选项:
A:Analysis of the physical and chemical processes occurring in process under consideration.
B:Writing of the differential (and other) equations describing the process under consideration.
C:Derivation of the conservation laws (integrals of motions) for the problem under consideration.
D:Analysis of physical units of each terms involving in the equations.
E:Developing finite-difference schemes (finite-elements scheme) for numerical solution of the problem under consideration.
F:Introducing dimensionless variables and writing similarity parameters (π – parameters).
G:Quality’s analysis of uniqueness solution or multiplicity of the problem solution. For this aim, as a rule, the pointwise model is derived from PDEs.
答案: 【
Writing of the differential (and other) equations describing the process under consideration.
】
2、 问题:Which of the following options is the requirement for the numerical method?( )。
选项:
A:High order of approximation of the differential equations by numerical solution.
B:FDS must be economical one. It means that 3D or 2D difference equations must be solved as sequence of 1D difference equations.
C:The numerical method must be tested by using the well-known solutions of the problem under consideration.
D:All of the above
答案: 【
All of the above
】
3、 问题:The following are applications of laser radiation in the field of physics?( )。
选项:
A:Nanophotonics
B:Astrophysics
C:Photochemistry
D:Optical data storage(CD, SVD, 5D optical memory)
答案: 【
Nanophotonics
Astrophysics
Optical data storage(CD, SVD, 5D optical memory)
】
4、 问题:What fields can laser radiation be used in?( )。
选项:
A:LaserBiology
B:Laser Chemistry
C:LaserMedicine
D:Physics
答案: 【
LaserBiology
Laser Chemistry
LaserMedicine
Physics
】
5、 问题:What are the properties of laser radiation?( )。
选项:
A:Polarization.
B:Divergence of laser beam is small.
C:Laser emits monochromatic wave. Usually laser emits single wavelength.
D:Stimulated emission.
E:Coherence (spatial, temporal).
答案: 【
Polarization.
Divergence of laser beam is small.
Laser emits monochromatic wave. Usually laser emits single wavelength.
Stimulated emission.
Coherence (spatial, temporal).
】
6、 问题:The one that can explain the experimental curve of blackbody radiation perfectly is ( )
选项:
A:the Riley-Pierce equation
B:Wien’s formula
C:Planck’s formula
D:Einstein’s formula
答案: 【
Planck’s formula
】
7、 问题:A concave cavity with a concave mirror of radius R equal to the cavity length L is a ( ).
选项:
A:Stabilizing cavity
B:Critical cavity
C:unsteady cavity
D:Uncertain
答案: 【
Critical cavity
】
8、 问题:The wavelength of the CO2 laser is( )
选项:
A:335nm
B:810nm
C:1064nm
D:10.6μm
答案: 【
10.6μm
】
9、 问题:The basic structure of the laser consists of electrical working matter, pump source and ( ) three parts.
选项:
A:Reflector
B:Window mirror
C:Affected pole
D:Optical resonant cavity
答案: 【
Optical resonant cavity
】
10、 问题:Carbon dioxide lasers commonly used gas mixture composition is composed of ( ), helium, argon, nitrogen.
选项:
A:Carbon monoxide
B:Carbon dioxide
C:Oxygen
D:Neon gas
答案: 【
Carbon dioxide
】
第二章 单元测试
1、 问题:What type of laser does the carbon dioxide laser belong to?( )
选项:
A:Gas laser
B:Fiber laser
C:Semiconductor laser
D:Solid-state laser
答案: 【
Gas laser
】
2、 问题:When the pulse energy is certain, the narrower the pulse width, it means the time energy density with time as the denominator ( ).
选项:
A:The greater
B:the smaller
C:Constant
D:Uncertain
答案: 【
The greater
】
3、 问题:For a uniformly broadened medium, the small-signal gain coefficient at the center center frequency is G0(v0), and when I=Is, saturation is significant, and the non-small-signal center-frequency gain coefficient is: ( ).
选项:
A: 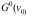
B: 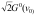
C: 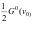
D: ![]()
答案: 【
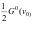
】
本文章不含期末不含主观题!!
本文章不含期末不含主观题!!
支付后可长期查看
有疑问请添加客服QQ 2356025045反馈
如遇卡顿看不了请换个浏览器即可打开
请看清楚了再购买哦,电子资源购买后不支持退款哦


